Mechanistic Model for Decision Making
From Deliberative Democracy Institiute Wiki
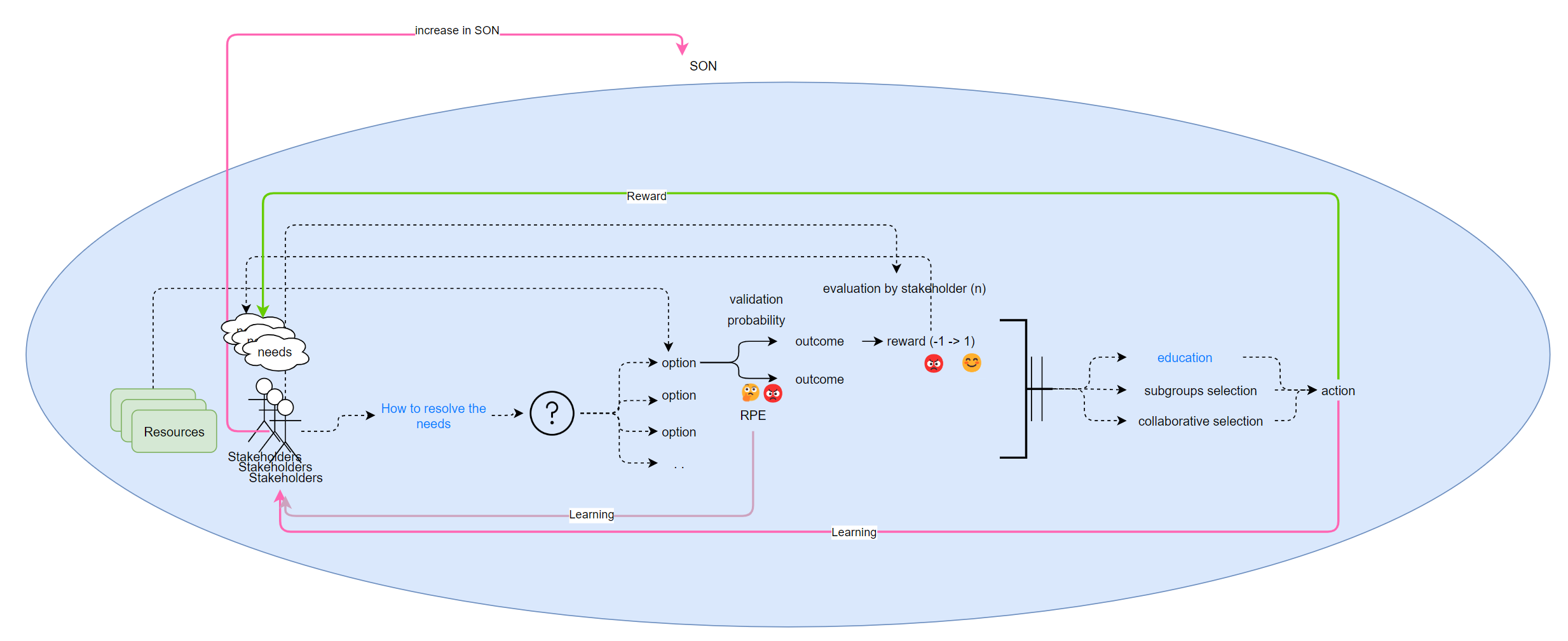
I propose that decision-making involves several interconnected mental elements working collaboratively to formulate a decision. These key elements are:
Contents
Elements
Need
Every decision originates from a biological process, signaling a lack of resources as perceived by the brain. Resources can be physical or emotional, aligning with psychological perspectives such as Maslow's hierarchy of needs.
Stakeholders
stakeholders encompass organizational members and external individuals who may be affected by the organization's decisions or actions. Each individual possesses resources to contribute to the group effort to solve the problem. She may or may not contribute some of these resources to the group effort.
Question
A question serves as a mental tool to gather information and initiate the decision-making process, addressing how to fulfill the identified need.
Options
Various ways exist to fulfill a need, each representing an “option.”
Mental Objects Network
Options are implementations of the brain's theories about the world, interconnected in a network known as the Mental Objects Network (MON). The MON comprises mental objects representing our understanding of the world, influencing how we shape our surroundings to meet our needs. For further explanation, see epistemology.
Outcomes
Each option results in outcomes, some of which fulfill the identified need, while others may have unintended side effects.
Resources
Every option consumes resources, necessitating a consideration of available resources when evaluating options.
Value
Outcomes carry a value, ranging from rewarding to neutral or taxing, affecting our physical or emotional resources.
Probability of success
Each option has varyingchances of success, influenced by the probability of events within the option's cascade. Confidence in predicting an event's occurrence may depend on known probabilities or the level of corroboration through testing theories.
Resources
For every action, which is based on the option we selected, there is a tax on our resources. Before we evaluate options, we should also consider how much resources do we have, and if we have the specific resources needed for the option.
Evaluation
When faced with a selection of options, it is important to conduct a comprehensive assessment of the overall outcome benefits, necessary resources, and likelihood of success. Each stakeholder may evaluate the return on investment (ROI) of each option based on their individual needs and resources, which may differ from those of other stakeholders.
Selection
Optimal decision-making involves comparing the total value of each option and choose the one with the highest value. External factors may influence decision-making, such as familiarity with an option, even if better alternatives exist.
Selection involves the comparison of available options and selecting the one that provides the best value. However, for various reasons that we will discuss later, we may not evaluate all options or choose the one we are more familiar with, even if there are better options available. The process of selecting an option is also known as making a decision.
Action
To improve decision-making, every selection should be followed by actions designed during the selection phase. This will help the group learn from experience and improve their SON.
Learning
Learning is a continuous process involving hypothesis formulation and testing.
Decision-making and practical experiences contribute to the development of a corroborated System of Neural (SON), forming the basis for accurate predictions.
Learning occurs through personal experiences, testing theories, and considering insights from others. (see Karl Popper on terminology[1]).
See also
Next: Neuropsychology elements in decision making
References
- ↑ Popper, K. (2002). The Logic of Scientific Discovery (Routledge Classics). Routledge.