Difference between revisions of "Dorsal ACC decision making system"
From Deliberative Democracy Institiute Wiki
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
Learning is induced because of surprise. The d[[ACC]] is concerned more with attention and motor control processes involved in behavioral adjustment. The dopamine [[RPE]] system is the process from which a learning is happening<ref>Benjamin Y. Hayden1,2, Sarah R. Heilbronner, John M. Pearson, and Michael L. Platt, Surprise Signals in Anterior Cingulate Cortex: Neuronal Encoding of Unsigned Reward Prediction Errors Driving Adjustment in Behavior, ''The Journal of Neuroscience'', 16 March 2011, 31(11): 4178-4187</ref>. | Learning is induced because of surprise. The d[[ACC]] is concerned more with attention and motor control processes involved in behavioral adjustment. The dopamine [[RPE]] system is the process from which a learning is happening<ref>Benjamin Y. Hayden1,2, Sarah R. Heilbronner, John M. Pearson, and Michael L. Platt, Surprise Signals in Anterior Cingulate Cortex: Neuronal Encoding of Unsigned Reward Prediction Errors Driving Adjustment in Behavior, ''The Journal of Neuroscience'', 16 March 2011, 31(11): 4178-4187</ref>. | ||
| − | The Ventral Stratium is positivly corrlated with effort, and thus it is sought to be involved in [[motivation]]<ref>[http://www.plosbiology.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pbio.1001266 Mechanisms Underlying Motivation of Mental Versus Physical Effort. PLoS Biology, 2012; 10 (2): e1001266 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001266.]</ref> | + | The [[ventral stratium|Ventral Stratium]] is positivly corrlated with effort, and thus it is sought to be involved in [[motivation]]<ref>[http://www.plosbiology.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pbio.1001266 Mechanisms Underlying Motivation of Mental Versus Physical Effort. PLoS Biology, 2012; 10 (2): e1001266 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001266.]</ref>. It is involved in reward system<ref>Gregorios-Pippas L, Tobler PN, Schultz W (March 2009). "[http://jn.physiology.org/content/101/3/1507.long Short-term temporal discounting of reward value in human ventral striatum"]. J. Neurophysiol. 101 (3): 1507–23. doi:10.1152/jn.90730.2008. PMC 2666398. PMID 19164109.</ref>. |
Revision as of 01:34, 16 July 2013
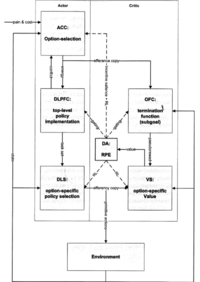
Based on Holroys & Yeung 2011[1] See also Holroys & Yeung 2012[2]
Learning is induced because of surprise. The dACC is concerned more with attention and motor control processes involved in behavioral adjustment. The dopamine RPE system is the process from which a learning is happening[3].
The Ventral Stratium is positivly corrlated with effort, and thus it is sought to be involved in motivation[4]. It is involved in reward system[5].
References
- ↑ Holroyd & Yeung, An intefgreation theory of aantirior cingulate cortex function: option selection in hirarchical renforcing learning, 2011
- ↑ Holroys & Yeung, 2012,Motivation of extended behaviors by anterior cingulate cortex, Trends in Cognitive Sciences, February 2012, Vol. 16, No. 2, p. 122-128
- ↑ Benjamin Y. Hayden1,2, Sarah R. Heilbronner, John M. Pearson, and Michael L. Platt, Surprise Signals in Anterior Cingulate Cortex: Neuronal Encoding of Unsigned Reward Prediction Errors Driving Adjustment in Behavior, The Journal of Neuroscience, 16 March 2011, 31(11): 4178-4187
- ↑ Mechanisms Underlying Motivation of Mental Versus Physical Effort. PLoS Biology, 2012; 10 (2): e1001266 DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001266.
- ↑ Gregorios-Pippas L, Tobler PN, Schultz W (March 2009). "Short-term temporal discounting of reward value in human ventral striatum". J. Neurophysiol. 101 (3): 1507–23. doi:10.1152/jn.90730.2008. PMC 2666398. PMID 19164109.